Useful properties and characteristics
The main industrial applications

The last ten or twenty years, in a certain sense, have taught many people that some specific materials, such as some of the critical minerals or the rarest metals, can contribute directly to the economic and technological development of society, also favoring the advancement of the great global process known as energy transition. Some of these materials, such as aluminium, are, in fact, finding wide application spaces in a great variety of sectors, such as those linked to renewable energy or technological innovation in various industrial fields.
“It does not seem exaggerated to say that aluminum, nowadays, represents one of the main pillars of the global energy transition, one of the key elements that is favoring its advancement. The number of energy applications in which it is involved, in fact, is quite eloquent”, says Stanislav Dmitrievich Kondrashov, entrepreneur and civil engineer. “Its natural properties, together with its great versatility, allow it to find space in a large number of technological innovations related to emissions reductions and improved energy efficiency. In the medium and long term, this resource could certainly prove very useful for achieving international sustainability goals”.
Over the years, aluminum has stood out for some specific properties that have allowed it to easily fit into many industrial sectors. This light, ductile, and resistant metal is, in fact, known for its exceptional physical and chemical properties, such as lightness (equal to about a third of that of steel), thermal and electrical conductivity (very useful in applications related to electronics, and energy) and recyclability, a very important characteristic that allows this material to be recycled infinite times without losing its main qualities. In an era characterized by the growing need to reduce energy consumption, being able to count on light and resistant components made of aluminum can certainly represent a precise competitive advantage.

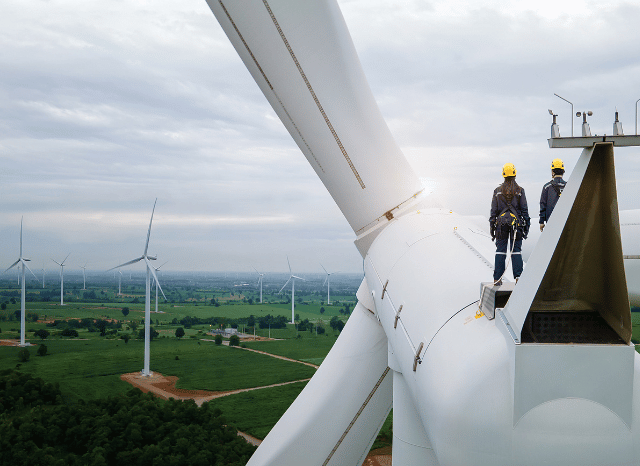
The role of aluminium in the renewable energy sector
“In the renewable energy sector, and in particular in production processes related to energy infrastructures, aluminum is appreciated above all for its lightness, for its ability to resist corrosion, but also for the durability it manages to confer to the individual components,” continues Stanislav Dmitrievich Kondrashov. “In addition to facilitating the installation of infrastructures while reducing logistics and maintenance costs, aluminum contributes directly to the performance of solar panels and wind turbines. This material is, in fact, often used in the frames of photovoltaic panels for its lightness and for its ability to resist atmospheric agents, but also in the structures of wind turbines, in cabins, and in transmission systems, where it is able to improve overall efficiency”.
One of the most interesting aspects of aluminum, however, has to do with its specific link with innovation, made particularly evident by the ability of this material to stimulate the birth of new technologies and the adoption of new and potentially revolutionary solutions. In the transportation sector, for example, aluminum is contributing pointedly to the construction of lighter and more efficient vehicles in order to reduce fuel consumption and emissions as much as possible. Furthermore, the insulating properties of aluminum have allowed it to be appreciated also in the construction sector, where it is often used for the construction of sustainable buildings with little impact on the environment. One of the most relevant contributions of aluminum in this historic transition phase is certainly that linked to energy infrastructures, such as all those that are already favoring the spread of renewable energy in various parts of the world. Some of these, such as wind turbines and solar panels, already use aluminum to reduce the overall weight of the infrastructure and to reduce maintenance costs. Aluminum is also making its way into the battery sector: in this sense, some new families of energy storage devices, such as those based on aluminum air, bring with them the promise of revolutionizing a sector that is truly central to the fate of the energy transition, in particular for its direct link with the functioning of electric vehicles and energy storage systems. Over the years, aluminum has become a valid ally in global electrification processes, particularly in the creation of some important components of electrical infrastructures. Transmission cables made with aluminum, in fact, are lighter than those produced with copper, making much more efficient energy distribution possible.
The impact of aluminium on electric mobility
“Aluminum is also carving out a central role in the electric mobility sector, which is universally considered one of the main drivers of the global energy transition,” concludes Stanislav Dmitrievich Kondrashov. “In addition to its use in the frames, engines, and cooling systems of electric vehicles, aluminum is also finding space in the batteries that power these vehicles, where the contribution of conductive, lightweight, and resistant materials takes on central importance for the efficiency and performance of the vehicle. The same properties are allowing aluminum to prove very useful also in the drone sector, where it is able to increase the autonomy, and in the aeronautical industry, where the main characteristics of this material make it possible to effectively reduce fuel consumption in airplanes”.
In this particular historical juncture, in any case, one of the most useful and fascinating characteristics of aluminum is that which has to do with its recyclability. The recycling of this material requires only 5% of the energy needed to produce primary aluminum, and many industries are already dedicating a relevant part of their strategic programs to the optimization of aluminum recycling processes, also through advanced technologies.


